بالنسبة لملايين الرجال في جميع أنحاء العالم، فإن تضخم البروستاتا الحميد (BPH) يعني حياة مضطربة بسبب التبول المتكرر، والحرمان من النوم، وانخفاض جودة الحياة. في حين أن العلاجات التقليدية غالباً ما تُجبر المرضى على الاختيار بين الأدوية غير الفعالة أو الإجراءات الجراحية الغازية ذات الآثار الجانبية الجراحية الكبيرة، فإن انصمام الشريان البروستاتي (PAE) يُقدم بديلاً ثورياً. يوفر هذا الإجراء طفيف التوغل تخفيفاً كبيراً للأعراض دون التسبُب في عجز جنسي، أو سلس البول، أو التعافي المُطول. باعتباره فعالاً بشكل خاص في علاج البروستاتا الأكبر حجماً والأعراض المزعجة لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد، يتطلب PAE تخديراً موضعياً فقط ويعود المرضى إلى الأنشطة الطبيعية في غضون يوم أو اثنين. اكتشف كيف يعمل هذا العلاج المتطور لـ علاج ورم البروستاتا الحميد (غدة البروستاتا) على إحداث تحول في إدارة المرض.
تضخم البروستاتا الحميد: تحدي صحي عالمي
تُمثل أعراض تضخم البروستاتا الحميد أحد أكثر التحديات الصحية انتشاراً بين الرجال حول العالم. يؤثر هذا التضخم غير السرطاني في غدة البروستاتا على ما يقرب من 45٪ من الرجال فوق سن 45 عاماً، مع زيادة انتشاره إلى حوالي 80٪ عند الرجال فوق سن 70 عاماً.
يختلف عبء تضخم البروستاتا الحميد بشكلٍ كبير عبر المناطق والحالات الاجتماعية والاقتصادية. تواجه المناطق المتوسطة SDI (المؤشر الاجتماعي الديموغرافي) العبء المُطلق الأثقل. تتحمل الفئة العمرية 65-69 عاماً العبء الأكبر على مستوى العالم، مع وجود اتجاهات متزايدة مثيرة للقلق في كل من الفئتين العمريتين 40-44 و 80+.
كما لاحظ فريقنا الطبي من خلال سنوات من البحث واستشارات المرضى، فإن تضخم البروستاتا الحميد يؤثر بشكلٍ كبير على جودة الحياة. ترتبط هذه الحالة بأعراض المسالك البولية السفلية (LUTS). كثيراً ما يُبلغ المرضى عن التبول الليلي المزعج، وانسداد البول، وضعف مجرى البول، وزيادة تكرار التبول – وكلها يمكن أن تُقلل بشكلٍ كبير من جودة الحياة، وتُضعف الصحة العقلية، وتؤدي إلى زيادة تكاليف الرعاية الصحية.
دفع هذا فريقنا الطبي إلى البحث نحو إيجاد علاجات أكثر أماناً وطفيفة التوغل تعمل على معالجة الآليات الأساسية مع الحفاظ على الوظيفة الفسيولوجية.
الإدارة التقليدية لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد
بالنسبة للعديد من المرضى، يمثل الدواء خط العلاج الأول لأعراض تضخم البروستاتا الحميد. تشمل الخيارات الدوائية الحالية ما يلي:
- حاصرات ألفا Alpha-blockers، التي تعمل عن طريق إرخاء العضلات الملساء في عنق المثانة والبروستاتا، مما يجعل التبول أسهل
- مثبطات مختزلة الألفا-5، والتي تعمل على تقليص حجم البروستاتا عن طريق منع التغيرات الهرمونية التي تسبب نمو البروستاتا
غالباً ما توفر الأدوية تخفيفاً بسيطاً للأعراض بينما من المحتمل أن تسبب آثاراً جانبية كبيرة، بما في ذلك العجز الجنسي والدوار وانخفاض ضغط الدم. يجد العديد من المرضى أيضاً أن الحاجة إلى الدواء مدى الحياة غير مرغوب فيها ويتعرضون لتناقص الفعالية بمرور الوقت. عندما تثبت الأدوية عدم فعاليتها، تتوفر خيارات جراحية مختلفة:
- استئصال البروستاتا المفتوح
- الاستئصال عبر الإحليل للبروستاتا (TURP)
- شقّ البروستاتا عبر الإحْليل (TUIP)
- Greenlight Laser therapy
- الاجتثاث بالليزر عبر العجان
- HoLEP
- الاجتثاث المائي
في حين أن الإجراءات الجراحية الشائعة يمكن أن تُخفف الأعراض بشكل فعال، إلا أنها تحمل مخاطر كبيرة من المضاعفات بما في ذلك النزيف، والقذف الرجوعي، وسلس البول، وضعف الانتصاب. تتطلب معظم الخيارات الجراحية أيضاً تخديراً عاماً، ودخول المستشفى، وفترات تعافي ممتدة.
البدائل طفيفة التوغل ظهرت أيضاً، مثل رفع الإحْليل البروستاتيّ (UroLift) و transurethral microwave therapy (TUMT) و rezum water vapor therapy. على الرغم من أنها أقل غزواً، إلا أن هذه الأساليب غالباً ما توفر نتائج أقل استدامة من الجراحة التقليدية، مع معدلات إعادة علاج أعلى. العديد منها غير مناسب للبروستاتا الأكبر حجماً (> 80 سم مكعب)، وبعضها يؤدي إلى تأخُر تَحسُن الأعراض.
أجبرت هذه القيود في العلاجات التقليدية فريقنا الطبي على البحث في خيارات علاجية أكثر توازناً يمكن أن توفر تخفيفاً فعالاً للأعراض دون المساس بالسلامة أو جودة الحياة. قادنا هذا البحث المُكثف إلى تحديد انصمام الشريان البروستاتي (PAE) كـ علاج غير دوائي لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد واعداً وبديلاً مناسب للعديد من الرجال.
بالنسبة للرجال الذين يعانون من أعراض الورم الغدي الحميد في البروستاتا الصعبة والذين يبحثون عن بديل للأدوية أو الجراحة التقليدية، يمثل PAE خياراً ثورياً مع الحد الأدنى من المخاطر والنتائج الممتازة.
انصمام الشريان البروستاتي: الجيل القادم في علاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد
انصمام الشريان البروستاتي لعلاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد يمثل نقلة نوعية في إدارة المرض، مما يوفر نتائج سريرية متفوقة مع الحد الأدنى من الغزو مقارنةً بالطرق التقليدية. على عكس الأدوية التي تعمل فقط على إدارة الأعراض أو الجراحات التي تُزيل الأنسجة، فإن هذا الإجراء الرائد يُقلل بشكل استراتيجي من تدفق الدم إلى البروستاتا المتضخمة، مما يؤدي إلى انكماش الأنسجة مع الحفاظ على الوظيفة البولية والجنسية.
*Pisco JM et al Eur Radiol 2013;23(9):2561
كيف يعمل PAE
أثناء مراحل الإجراء، يقوم أخصائي الأشعة التداخلية للبروستاتا بالوصول إلى النظام الشرياني من خلال ثقب صغير في الشريان الفخذي تحت التخدير الموضعي. باستخدام تقنيات التصوير المتخصصة، بما في ذلك تصوير الأوعية بالطرح الرقمي والتصوير المقطعي المحوسب بالأشعة المخروطية، ينقل الأخصائي قسطرة دقيقة إلى شرايين البروستاتا التي تُغذي أنسجة البروستاتا المتضخمة. ثم يتم بعد ذلك حقن جزيئات صمية صغيرة (عادةً 100-500 μm) لسد (إحصار) هذه الشرايين، مما يُقلل من تدفق الدم إلى البروستاتا.
يعمل PAE من خلال آليات تآزرية متعددة تجعله فعالاً بشكلٍ خاص:
- الاحتشاء الإقفاري يؤدي إلى انكماش غدة البروستاتا المتضخمة
- استرخاء العضلات الملساء المتزايدة في البروستاتا من خلال إزالة التعصيب الأدرينالي-ألفا α-adrenergic denervation (على غرار عمل حاصرات ألفا alpha-blockers)
- استرخاء خلايا العضلات الملساء بواسطة أكسيد النيتريك (مُشابه للمداواة بالأعشاب)
- انقطاع محور التستوستيرون، مما يوفر الحرمان من الأندروجين (على غرار تثبيط التقدُم بواسطة المثبطات المختزلة 5α)
- موت الخلايا المبرمج بواسطة نقص التروية لخلايا البروستاتا
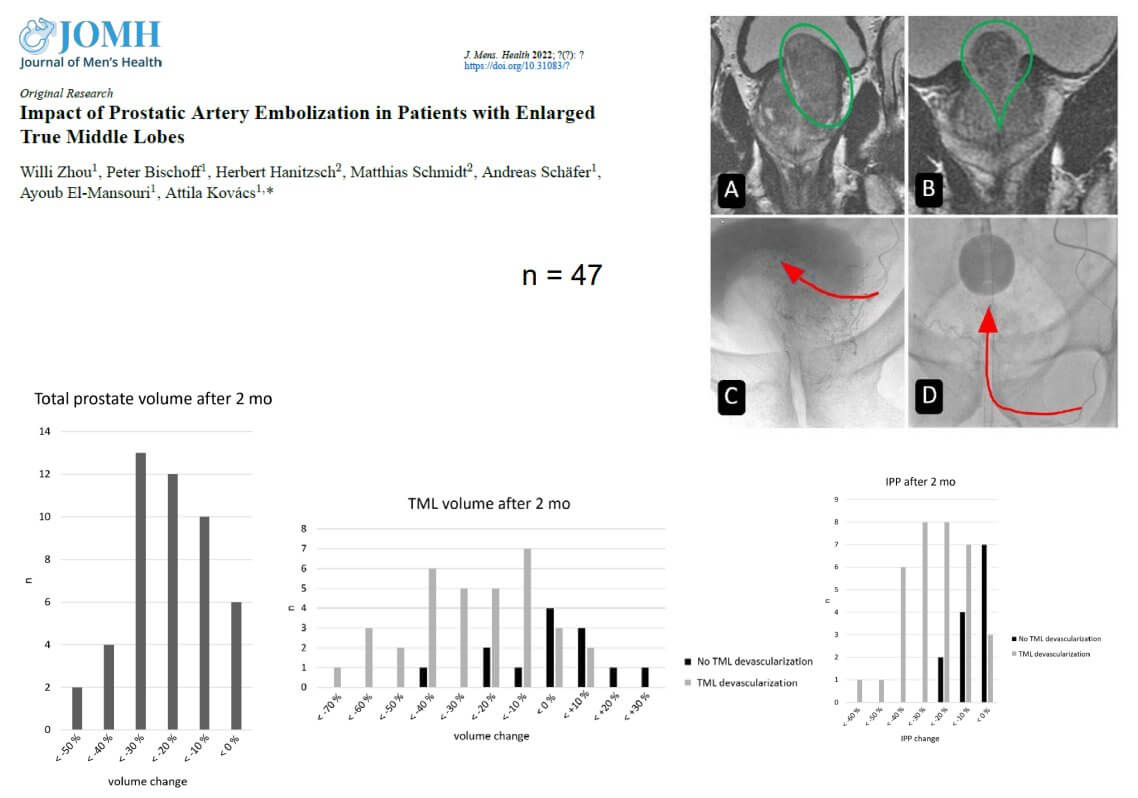
يسمح هذا النهج متعدد الأوجه لـ PAE بـ توفير تخفيف فوري للأعراض وتخفيض مستدام في حجم البروستاتا بمرور الوقت. من المهم أن نلاحظ أن PAE يمكن أن يُقلل بشكل فعال من الهياكل البروستاتية المحددة التي تُسبب الانسداد، بما في ذلك بروز البروستاتا داخل المثانة (IPP)، والفص الأوسط الحقيقي (TML)، والتي غالباً ما تكون من الأسباب الرئيسية لانسداد مخرج المثانة وأعراض التخزين التي تُزعج المرضى بشكلٍ خاص.
المُرشحون المثاليون لهذا الإجراء
يُعتبر PAE مناسباً بشكلٍ خاص لما يلي:
- المرضى الذين يعانون من أعراض متوسطة إلى شديدة في المسالك البولية السفلية (LUTS) كما تم قياسها بواسطة درجة أعراض البروستاتا الدولية (IPSS)
- المرضى الذين يعانون من ضعف جودة الحياة بسبب أعراض تضخم البروستاتا الحميد
- أولئك الذين لم يستجيبوا بشكل كافٍ للعلاج الطبي لمدة 6 أشهر على الأقل
- المرضى غير المرشحين للجراحة أو الذين رفضوا التدخل الجراحي
- الرجال الذين لديهم أحجام البروستاتا أكبر من 80 سم مكعب وهي كبيرة جداً بالنسبة لـ TURP التقليدي وما إلى ذلك.
- المرضى الذين يتعرضون لاحتياجات علاج احتباس البول
حددت الأبحاث عدة تنبؤات لنتائج سريرية أفضل مع PAE، بما في ذلك العمر أقل من 65 عاماً، ونجاح PAE الثنائي (علاج كلا جانبي البروستاتا)، وانخفاض خط الأساس IPSS، والمرضى الذين يعانون من احتباس البول. من الجدير بالذكر أن المرضى الذين لديهم بروستاتا أكبر حجماً (>80 مل) غالباً ما يشهدون انخفاضاً أكبر في الحجم (42.3٪ مقابل 28.9٪) وتحسناً في الأعراض مقارنةً بمن لديهم بروستاتا أصغر.
*بيانات البروفيسور الدكتور في الطب أتيلا كوفاكس
كان وجود الفص الأوسط الحقيقي (TML) يُعتبر في السابق موانع نسبية لـ PAE. ومع ذلك، فقد أظهرت الدراسات السريرية الحديثة باستمرار أن PAE فعال كـ إجراء لتخفيف المشاكل الناجمة عن زيادة حجم TML بنسبة 32.1٪ تقريباً عندما يتم انصمام TML بنجاح، مع تحسينات مقابلة في الأعراض وتدفق البول.
المزايا الرئيسية مقارنةً بالطرق التقليدية
توفر الأشعة التداخلية وانصمام الشريان البروستاتي العديد من المزايا المهمة مقارنةً بعلاجات تضخم البروستاتا الحميد التقليدية:
- إجراء طفيف التوغل يتم إجراؤه تحت التخدير الموضعي
- عدم وجود خطر من الآثار الجانبية المرتبطة بـ TUR مثل القذف الرجوعي، أو سلس البول، أو العجز الجنسي
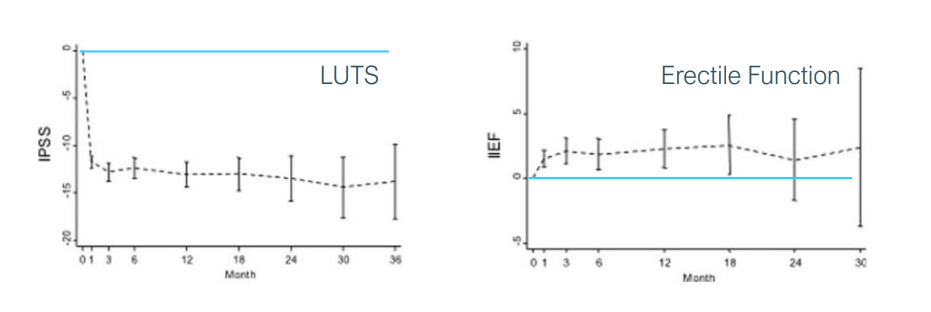
- تأثير فوري، مع بدء تحسن LUTS بعد 5-8 أيام فقط
- تأثير مستدام يستمر في التقدُم على مدى الأشهر الستة التالية
- القدرة على تقليل أو التوقف عن استخدام الأدوية
- فعال بشكل خاص لأعراض التخزين (الإلحاح، والتبول الليلي)، والتي غالباً ما تكون الأكثر إزعاجاً للمرضى ولكنها تتحسن بشكل أقل مع الجراحة التقليدية
- مناسب بشكل استثنائي للمرضى الذين لديهم بروستاتا أكبر حجماً (>80 سم مكعب) والذين ليسوا مرشحين مثاليين لـ TURP
- معدل إعادة العلاج منخفض جداً أقل من 1٪ بعد 5 سنوات
- الحد الأدنى من الآثار الجانبية، حيث يعاني حوالي 8.5٪ فقط من المرضى من متلازمة ما بعد الانصمام الخفيفة التي يمكن إدارتها بفعالية باستخدام الأدوية المضادة للالتهاب غير الستيرويدية
كما وجد فريق البحث لدينا، فإن الميزة الأكثر أهمية لـ PAE ربما تكون ملف الآثار الجانبية المواتية. تُشكل المخاطر المتعلقة بالنزيف ومضاعفات التخدير أثناء الجراحة، إلى جانب المخاطر متوسطة المدى لسلس البول، والتأثيرات على الوظيفة الجنسية، والقذف الرجوعي المرتبطة بالعلاجات التقليدية، مخاوف جدية للعديد من المرضى. إن قدرة PAE على تجنُب هذه المضاعفات تؤدي إلى ارتفاع مستوى رضا المرضى.
النتائج المتوقعة والجدول الزمني للتعافي: العلاجات التقليدية مقابل العلاجات الجديدة
تختلف طرق علاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد بشكلٍ كبير من حيث النتائج، والجداول الزمنية للتعافي، والتأثير العام على جودة حياة المرضى. استناداً إلى أبحاثنا وخبرتنا السريرية، وجدنا أن PAE يوفر توازناً مقنعاً بين الفعالية والحد الأدنى من الإزعاج لحياة المرضى.
| العلاج | تخفيض الحجم | تحسُن الأعراض (IPSS) | وقت التعافي | الآثار الجانبية | معدل إعادة العلاج (5 سنوات) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الأدوية | الحد الأدنى أو لا يوجد | متغير، وغالباً ما يكون معتدل | لا يوجد (علاج مستمر) | متغيرة، تشمل العجز الجنسي، والدوخة | لا ينطبق (علاج مستمر) |
| TURP | 30 - ٪80 | تخفيض بمقدار 10-15 نقطة | 2 - 4 أسابيع | معتدلة (قذف رجوعي في 65 - 75٪، ونزيف، وفترة تعافي أطول) | 10.3 - ٪11.6 |
| الاجتثاث المائي | 30 - ٪35 | تخفيض بمقدار 10-12 نقطة | 1 - 2 أسابيع | خفيفة (قسطرة، ونزيف) | حوالي 1٪ |
| الاجتثاث ببخار الماء | 15 - ٪30 | تخفيض بمقدار 10-12 نقطة | 3 - 5 أيام | خفيفة (أعراض بولية مؤقتة) | 4.4 - ٪7.5 |
| PAE | ما يصل إلى 42٪ للبروستاتا > 80 سم مكعب | تخفيض بمقدار 10-15 نقطة | 1 - 2 أيام | طفيفة (شعور موضعي مؤقت بعدم الارتياح) | أقل من 1٪ |
*بيانات Booking Health
يُظهر PAE نتائج مثيرة للإعجاب بشكلٍ خاص في العديد من المجالات الرئيسية:
- تصغير حجم البروستاتا: أظهرت الدراسات انخفاضا متوسطاً بنسبة 25.8٪ بشكلٍ عام، مع انخفاض أكبر (42.3٪) لدى المرضى الذين يعانون من البروستاتا الأكبر حجماً (> 80 سم مكعب)
- بروز البروستاتا داخل المثانة (IPP): تم تقليله بنجاح بنسبة 29.3٪ في المتوسط عندما يكون الإجراء ناجحاً من الناحية الفنية، مما يعالج أحد الأسباب الرئيسية لانسداد مخرج المثانة
- تحسُن الأعراض: انخفاضات كبيرة في درجات (IPSS (10-15 نقطة، وخاصةً بالنسبة لأعراض التخزين مثل الإلحاح والتبول الليلي التي يجدها المرضى الأكثر إزعاجاً
- جودة الحياة: تحسينات كبيرة في درجات جودة الحياة
- تدفق البول: زيادة في معدل التدفق الأقصى بمقدار 4.5-6 مل/ثانية، مع تحسينات أكبر لدى المرضى الذين يعانون من البروستاتا الأكبر حجماً
- البول المتبقي: انخفاض بمقدار 60-80 مل في حجم البول المتبقي بعد التبول
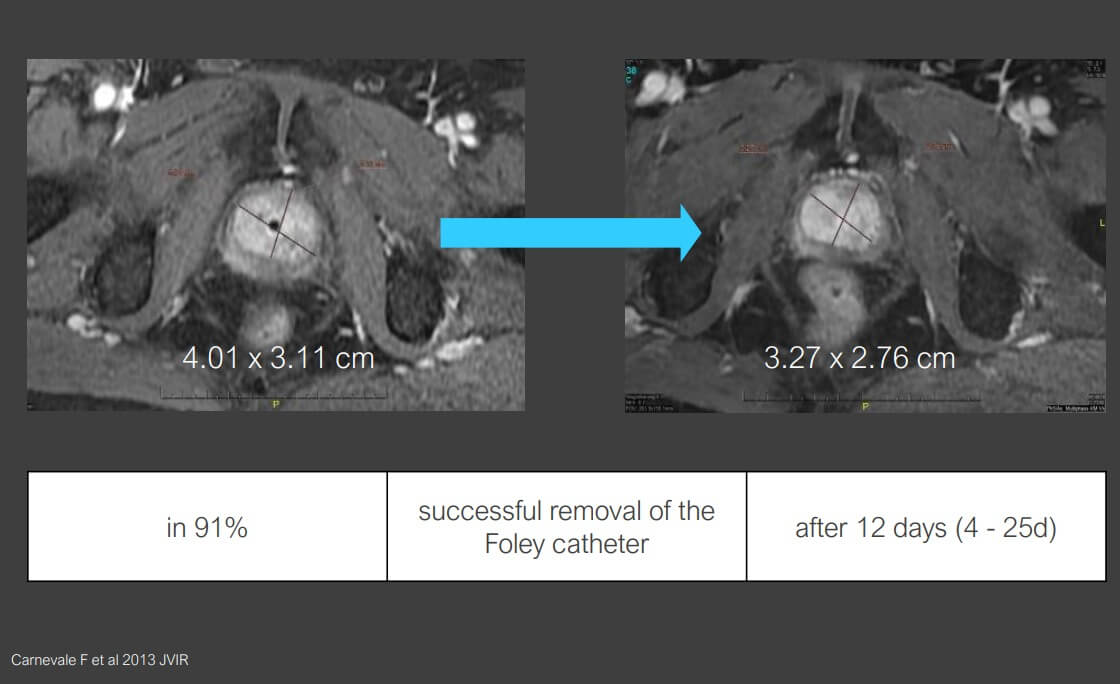
يُعتبر التعافي بعد PAE سريعاً بشكل ملحوظ مقارنةً بالعلاجات التقليدية. يتعرض معظم المرضى للشعور بعدم الارتياح الخفيف الخفيفة لمدة 24 إلى 48 ساعة فقط، والذي يمكن إدارته بشكل فعال باستخدام مسكنات الألم التي لا تستلزم وصفة طبية. يمكن للعديد من المرضى العودة إلى ممارسة أنشطتهم الطبيعية خلال يوم أو يومين، مقارنةً بأسابيع التعافي المطلوبة بعد التدخلات الجراحية.
الأهم من ذلك، أنه في حين أن تحسُن أعراض المسالك البولية السفلية LUTS يبدأ في غضون 5-8 أيام بعد انصمام الشريان البروستاتي PAE، فإن الفوائد تستمر في التَقدُم على مدار 6 أشهر مع تقلص البروستاتا تدريجياً، مما يوفر راحة مستدامة طويلة الأمد.
الوصول إلى إجراء PAE ذات المستوى العالمي مع Booking Health
التوفر المحدود للعلاجات المبتكرة مثل انصمام الشريان البروستاتي لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد يخلق حواجز كبيرة أمام المرضى الذين يبحثون عن بدائل للإدارة التقليدية لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد. في Booking Health، جعلنا مهمتنا هي سد هذه الفجوة من خلال إيصال المرضى بالخبرة المتخصصة اللازمة لهذه التدخلات المتطورة، مما يُبسط الوصول إلى الرعاية الطبية الدولية.
يستمر سوق علاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد في التطور مع وجود طرق مبتكرة مثل PAE الذي يحظى بالاعتراف في جميع أنحاء العالم. يتطلب هذا الإجراء خبرة واسعة في العلاج بالانصمام، ومعرفة تفصيلية بتشريح الأوعية الدموية البروستاتية المعقدة، وأنظمة التصوير المتقدمة بما في ذلك تقنية التصوير المقطعي المحوسب بالأشعة المخروطية لتحقيق السلامة والفعالية. نحن نُقدم الدعم الشامل للمرضى الذين يسعون للحصول على PAE من خلال نهج شخصي يتضمن:
- تقييم الخبراء لكل حالة والاتصال بالمرافق المتخصصة التي تضم أخصائيين تداخليين ذوي خبرة
- تطوير برامج العلاج الفردية في مراكز معترف بها دولياً دون فرض رسوم على المرضى الأجانب
- استكمال التنسيق الطبي واللوجستي بما في ذلك الوثائق، والمواعيد، والتغطية التأمينية الطبية
- دعم السفر مع خدمات النقل، والإقامة، والمترجم الفوري عند الحاجة
- العلاج الداعم وإدارة الرعاية المستمرة بما في ذلك شراء الأدوية والتواصل مع المتخصصين بعد العلاج
تشخيص الورم الغدي الحميد في البروستاتا وتحديد خيارات العلاج المناسبة يتطلب تقييماً دقيقاً. من خلال الشراكة مع Booking Health، يمكنك الوصول إلى مراكز التميز والمتخصصين الذين يتمتعون بالمهارات الفنية اللازمة لإجراء PAE بأمان وفعالية.
التزامنا الأساسي هو سلامتك وضمان حصولك على أفضل وقاية وعلاج. من خلال تسهيل الوصول إلى التدخلات المتخصصة، نأمل في توسيع إمكانيات علاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد لديك ودعم رحلتك العلاجية نحو تحسين صحة البروستاتا وجودة الحياة.
كل مريض له قصة: رحلات Booking Health العلاجية التي تُلهم
الأسئلة الشائعة لمرضانا
تضخم البروستاتا الحميد (BPH) هو تضخم غير سرطاني في غدة البروستاتا يؤثر على 45٪ من الرجال فوق سن 45 و 80٪ من الرجال فوق سن الـ 70، مما يُسبب أعراض بولية مثل التبول المتكرر، وصعوبة بدء التبول، وعدم إفراغ المثانة بالكامل.
يعتمد أفضل علاج لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد على شدة الأعراض وحجم البروستاتا، بدءاً من الأدوية مثل حاصرات ألفا alpha-blockers إلى الإجراءات طفيفة التوغل مثل انصمام الشريان البروستاتي، والذي يوفر تخفيفاً فعالاً للأعراض مع آثار جانبية أقل وتعافي أسرع.
تتضمن العديد من خيارات علاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد الجديدة العلاجات المُركبة ومثبطات PDE5، على الرغم من أن هذه الأدوية توفر عادةً تخفيفاً متواضعاً للأعراض وقد تُسبب آثاراً جانبية، مما يدفع العديد من المرضى إلى البحث عن بدائل تداخلية أكثر فعالية.
لا، لا يُزيد تضخم البروستاتا الحميد من خطر الإصابة بسرطان البروستاتا. على الرغم من أن كلاهما أصبح أكثر شيوعاً مع التقدم في السن، إلا أنهما يمثلان حالات مختلفة مع عوامل خطر وآليات خلوية مختلفة.
عند اختيار علاج تقليدي أو علاج جديد لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد، يجب مراعاة حجم البروستاتا، وشدّة العلامات والأعراض، والأمراض المصاحبة، والتفضيلات فيما يتعلق بالآثار الجانبية، ووقت التعافي، والآثار على الوظيفة الجنسية.
تُقدم علاجات جديدة لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد مزايا تشمل تقليل مخاطر العجز الجنسي، وفترات تعافي أقصر، ومضاعفات أقل مقارنةً بخيارات الجراحة التقليدية، مع توفير تَحسُن مماثل في الأعراض دون مخاطر النزيف، والقذف الرجوعي، وسلس البول.
يتضمن أحدث علاج لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد انصمام الشريان البروستاتي، والاجتثاث المائي، والعلاج ببخار الماء Rezum، ورفع الإحْليل البروستاتيّ UroLift، والعلاجات بالليزر، وكلها مُصممة لتقليل حجم البروستاتا أو تخفيف الانسداد مع الحد الأدنى من الآثار الجانبية ووقت التعافي.
انصمام الشريان البروستاتي هو إجراء غير جراحي يُستخدم لعلاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد عن طريق منع تدفق الدم إلى البروستاتا، مما يؤدي إلى انكماشها. يشمل المُرشحون المثاليون الرجال الذين يعانون من أعراض شديدة لا تستجيب للأدوية، والذين يعانون من البروستاتا أكبر من 80 سم مكعب، والمرضى الذين يعطون الأولوية للحفاظ على الوظيفة الجنسية.
العلاج بالاجتثاث المائي هو علاج جديد لورم البروستاتا الغدي باستخدام نفث الماء الذي يتم التحكم فيه عن طريق الروبوت والذي يتم توجيهه بواسطة التصوير بالموجات فوق الصوتية لإزالة أنسجة البروستاتا بدقة، مما يوفر آثاراً جانبية جنسية أقل، وإقامة أقصر في المستشفى، وفعالية العلاج بغض النظر عن حجم البروستاتا.
يظل العلاج بالليزر علاج بديل لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد قابل للتطبيق، حيث يوفر خطراً أقل للنزيف وفترة أقصر للقسطرة مقارنةً بـ TURP التقليدي، في حين أن الخيارات الأحدث مثل PAE قد تحافظ بشكلٍ أفضل على الوظيفة الجنسية وتتجنب التخدير العام للمرشحين المناسبين.
تحمل معظم خيارات العلاج غير الجراحي لتضخم البروستاتا الحميد مخاطر أقل من الجراحة التقليدية، مع احتمال تَسبُب PAE في ألم خفيف مؤقت، والاجتثاث المائي aquablation يتطلب القسطرة، ويتسبب Rezum في تفاقم الأعراض بشكلٍ مؤقت.
اختر العلاج في الخارج وستحصل بالتأكيد على أفضل النتائج!
المؤلفون:
تم تحرير المقال من قبل خبراء طبيين وأطباء معتمدين من مجلس الأطباء الدكتورة ناديجدا إيفانيسوفا و الدكتور فاديم جيلوك. لعلاج الحالات المشار إليها في المقال، يجب استشارة الطبيب؛ المعلومات الواردة في المقالة ليست مخصصة للتطبيب الذاتي!
سياستنا التحريرية، التي توضح بالتفصيل التزامنا بالدقة والشفافية، متاحة هنا. انقر على هذا الرابط لمراجعة سياساتنا.
المصادر:
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
اقرأ:
HoLEP - علاج تضخم البروستاتا الحميد (BPH) في يومين بدون ألم وبدون مضاعفات
قائمة المقالات:
لا تعرف من أين تبدأ؟
اتصل بـ Booking Health